This is a hard one. This problem is aimed to make sure that you know that 0 is an even integer although it is neither positive nor negative.
When dealing with exponents there are some things to take into account:
> Even exponents change the sign of the base; odd exponents don't.
> For positive fractions, no matter if the exponent is odd or even the result will always be smaller than the original base.
> For negative fractions, if the exponent is even the result will actually be bigger than the original base, since although the absolute value of the fraction actually decreases the sign changes and becomes positive. For instance:

(-\frac{1}{2})^2 = \frac{1}{4}[/m].

Having a cube implies that in terms of sign, whatever holds true for
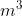
holds also true for
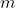
.
If m is greater than 1,
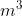
will also be greater than 1. If m is smaller than 1,
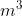
will also be smaller than one. The question can be restated as: is
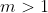
?
Statement 1:
If p is even:
for

,

,

; greater than 1.
for

,

m = 2 + \frac{1}{4} = \frac{9}{4}[/m]; greater than 1.
for
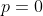
,

;
EQUAL TO 1.
Not sufficient.
Statement 2:
For

to be

,
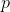
also has to be

.
for

,

m = 1 -\frac{1}{2} = \frac{1}{2}[/m]; smaller than 1.
for

,

m = 2 + \frac{1}{4} = \frac{9}{4}[/m]; greater than 1.
Not sufficient.
Both together:
p is even and negative. 0 is even integer is an even integer although it is neither positive nor negative.
for p = -2, -4, -6, etc..., m is always greater than 1.
Answer is C: both together are sufficient.